Different Types of User Roles in WordPress – How to Create, Edit and Delete Them
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Last updated on March 26th, 2024 at 07:06 am
Do you want to know “Different Types of WordPress User Roles and How to Create, Edit or Delete Them”?
Just like a team working on a project, a WordPress website has different roles for its users.
These roles determine who can do what on the site. Understanding these roles is like knowing each team member’s job – it keeps things organized and secure.
Picture your WordPress site as a busy kitchen. If everyone tries to cook, chaos ensues.
User roles, like chef and waiter, help in assigning specific tasks.
In fact, 83% of hacked WordPress sites are due to outdated plugins or themes, often because users had too many permissions.
Assigning the right roles reduces the risk of mishaps and keeps your site safe.
5 Different Types of User Roles in WordPress
1. Administrator Role
Think of the Administrator as the superhero of your WordPress website.
They have the power to do everything – publish content, install themes, and even change other users’ roles.
It’s like being the captain of the WordPress ship.
About 47% of all WordPress websites have at least one Administrator.
2. Editor Role
Editors are like the content managers. They can create, edit, and delete any post or page on your WordPress site.
It’s like having someone in charge of the story-telling part of your website.
Almost 20% of WordPress websites have Editors.
They play a crucial role in keeping the content ship sailing smoothly.
3. Author Role
Authors in WordPress are like the storytellers.
They can write, edit, and publish their own posts, but they can’t meddle with other people’s stories.
It’s like having individual authors in a magazine – each one has their space to share their tales.
Roughly 18% of WordPress sites have Authors, making them an essential part of the content creation team.
4. Contributor Role
Contributors are the idea generators.
They can write and edit their own posts, but they need an Editor or Administrator to approve and publish them.
It’s like having guest writers who submit their pieces, and the editor decides which ones make it to print.
About 6% of WordPress websites have Contributors, adding diverse perspectives to the content mix.
5. Subscriber Role
Subscribers are the audience.
They can read, leave comments, and update their profiles, but they can’t create or edit content.
It’s like having a group of dedicated readers who engage with your content.
A whopping 86% of WordPress websites have Subscribers.
They may not write the stories, but they are crucial for creating a thriving and interactive community around your content.
WordPress User Roles – Create, Edit and Delete
On many sites, you’ll see more than one of some roles listed because more than one role was assigned at some point during the configuration of the site.
1. Log into your site’s administration panel by entering the address for your blog followed immediately by /wp-admin into the location bar of your browser.
If you have changed the default name for your installation, then enter that instead.
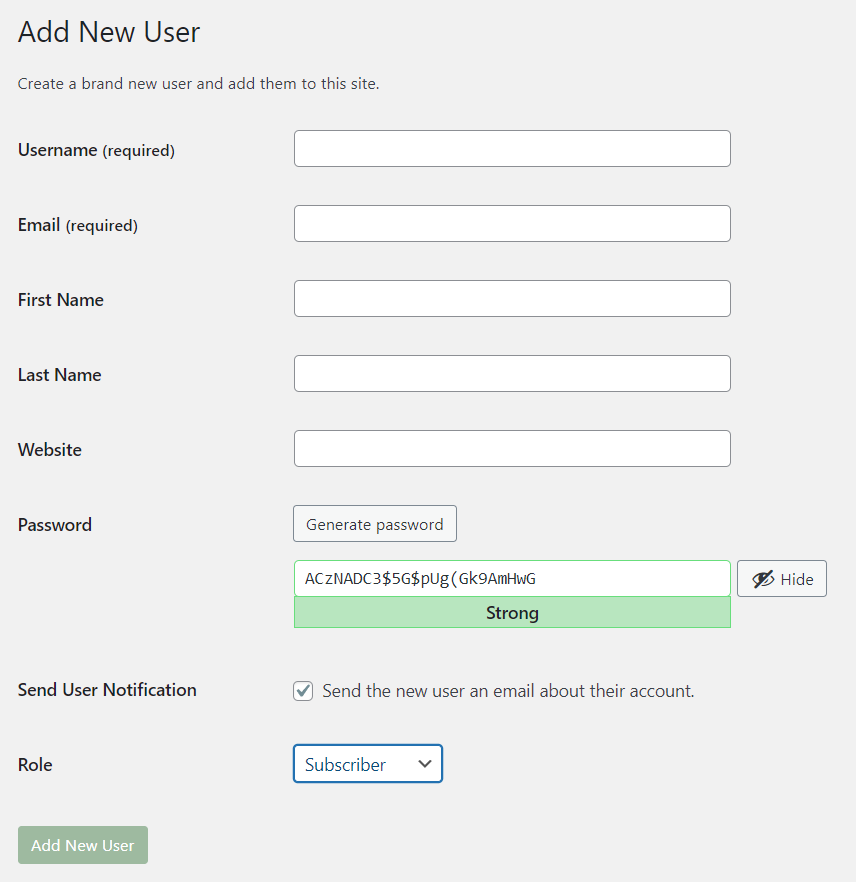
2. Once the main WordPress menu appears on the screen, choose “Users” from the left-hand nav and select “Add New”.
This will present the user registration form to add a new user.
3. On this page you will see several options for assigning a role to each new user.
Select one of these from the dropdown box labelled “Role” and click on the button marked “Add New User”.
4. On the next page, enter a username for the new user as well as an email address they can use to reset their password if they forget it in the future.
There are several options available for all of these fields but you can leave most of them blank for now.
5. Scroll further down the page until you see the section labelled “Role” which will contain all available roles to choose from.
Select one of these and then click on the button marked “Add User”.
You will return to the main Users screen where your newly registered user is waiting with their username and role already assigned.
6. Now that the user has been added, you can set up their additional profile options like first name and last name by clicking on their username or the “Edit” link next to it.
You can change their role any time if needed but for now, they are safe with the default Subscriber role assigned to them.
7. Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on the button marked “Update Profile”.
8. In future you can create, edit and delete the user from the same process.
Wrapping Up – WordPress User Roles
Understanding WordPress user roles is like knowing who’s who on your website.
It’s like having different keys for different people. Some have full control, others can only do specific things.
This helps keep your site safe and organized.
Whether you’re the boss, a writer, or just a visitor, knowing your role makes everything run smoother.